Introduction
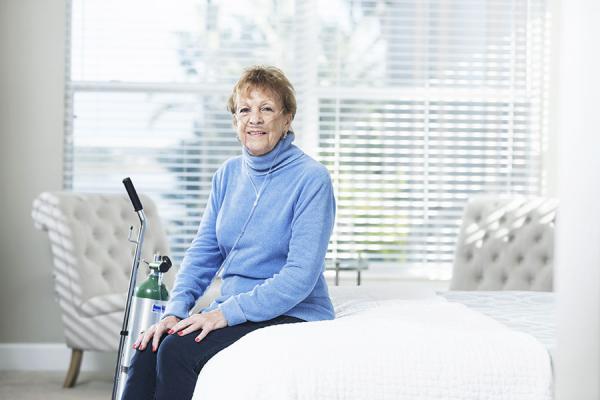
For individuals with respiratory conditions or low oxygen levels, receiving adequate oxygen therapy is crucial to improve their quality of life. While oxygen therapy was traditionally administered in clinical settings, advancements in medical technology have made it possible for individuals to receive oxygen therapy at home. In this article, we will explore the equipment used for oxygen therapy at home, its benefits, and how it enhances the well-being of patients.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Oxygen Therapy at Home
- Equipment for Oxygen Therapy at Home
- 2.1 Oxygen Concentrators
- 2.2 Oxygen Cylinders
- 2.3 Liquid Oxygen Systems
- Benefits of Oxygen Therapy at Home
- 3.1 Increased Independence and Mobility
- 3.2 Enhanced Comfort and Convenience
- 3.3 Improved Quality of Life
- How to Access Oxygen Therapy at Home Equipment
- 4.1 Consultation with Healthcare Provider
- 4.2 Prescription and Equipment Selection
- 4.3 Training and Education
- Caring for Oxygen Therapy Equipment
- 5.1 Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
- 5.2 Proper Storage and Handling
- 5.3 Monitoring Oxygen Levels
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- FAQ 1: Can I travel with oxygen therapy equipment?
- FAQ 2: Do I need a prescription for oxygen therapy at home?
- FAQ 3: Can I use oxygen therapy equipment without medical supervision?
- FAQ 4: How long does oxygen therapy at home typically last?
- FAQ 5: Can I adjust the oxygen flow rate myself?
Understanding Oxygen Therapy at Home
Oxygen therapy involves administering supplemental oxygen to individuals who have low oxygen levels in their blood. This therapy aims to increase the oxygen supply to the body and vital organs, alleviating symptoms and improving overall health. While oxygen therapy was traditionally administered in hospitals or clinics, advancements in medical equipment have made it possible for individuals to receive this therapy in the comfort of their own homes.
Equipment for Oxygen Therapy at Home
2.1 Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are the most common and convenient equipment used for oxygen therapy at home. These devices extract oxygen from the surrounding air, concentrate it, and deliver it to the patient through nasal cannulas for oxygen masks. Oxygen concentrators are compact, easy to use, and require a power source. They provide a continuous flow of oxygen, allowing individuals to receive therapy throughout the day and night.
2.2 Oxygen Cylinders
Oxygen cylinders are portable tanks filled with compressed oxygen. They are suitable for individuals who require oxygen therapy on the go or during outdoor activities. Oxygen cylinders provide a finite amount of oxygen and need to be refilled or replaced when empty. They come in various sizes to accommodate different oxygen requirements and are often used in conjunction with a portable oxygen regulator and delivery system.
2.3 Liquid Oxygen Systems
Liquid oxygen systems store oxygen in a liquid state at very low temperatures. These systems are typically used for individuals who require higher oxygen flow rates or have greater mobility needs. Liquid oxygen is stored in a reservoir and can be delivered to the patient through a stationary unit or a portable container. Liquid oxygen systems offer longer-lasting oxygen supply compared to concentrators or cylinders.
Benefits of Oxygen Therapy at Home
3.1 Increased Independence and Mobility
Oxygen therapy at home enables individuals to maintain their independence and mobility. With portable oxygen concentrators or cylinders, patients can engage in daily activities, attend social events, and even travel while receiving the necessary oxygen therapy. This freedom improves their overall well-being and reduces feelings of isolation or confinement.
3.2 Enhanced Comfort and Convenience
Receiving oxygen therapy at home provides a familiar and comfortable environment for patients. They can receive treatment while relaxing in their own living spaces, surrounded by their personal belongings. Home-based oxygen therapy eliminates the need for frequent visits to hospitals or clinics, saving time and reducing the inconvenience of travel.
3.3 Improved Quality of Life
Oxygen therapy at home plays a vital role in improving the quality of life for individuals with respiratory conditions. By ensuring an adequate supply of oxygen in breathing air, it helps alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and cognitive impairment. This therapy enables patients to engage in daily activities, sleep better, and experience an overall improvement in their physical and mental well-being.
How to Access Oxygen Therapy at Home Equipment
4.1 Consultation with Healthcare Provider
To access oxygen therapy at home equipment, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a pulmonologist or respiratory therapist. They will evaluate the individual’s condition, perform necessary tests, and determine if oxygen therapy is required. The healthcare provider will guide the patient through the process of obtaining the necessary equipment.
4.2 Prescription and Equipment Selection
Based on the evaluation, the healthcare provider will provide a prescription for oxygen therapy. This prescription specifies the oxygen flow rate and the type of equipment required. The patient, along with the healthcare provider and a home medical equipment provider, will determine the most suitable equipment, such as an oxygen concentrator or cylinders, based on individual needs.
4.3 Training and Education
Once the equipment is obtained, the patient and their caregivers will receive training on its proper usage, maintenance, and safety precautions. This training ensures that the patient can effectively operate the equipment and understand important guidelines, such as maintaining proper oxygen flow rates, cleaning the equipment, and recognizing potential issues or emergencies.
Caring for Oxygen Therapy Equipment
5.1 Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Proper cleaning and maintenance of oxygen therapy equipment are crucial to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cleaning the equipment, replacing filters, and performing routine maintenance tasks. Regular cleaning and maintenance contribute to the equipment’s optimal performance and prevent the risk of contamination or malfunctions.
5.2 Proper Storage and Handling
When not in use, oxygen therapy equipment should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area. Ensure that the equipment is protected from extreme temperatures, moisture, and direct sunlight. Follow proper handling procedures, such as avoiding dropping or mishandling the equipment, to prevent damage.
5.3 Monitoring Oxygen Levels
Regularly monitor the oxygen levels and ensure an adequate supply for continuous therapy. Check the oxygen concentrator or cylinder pressure gauge and keep track of the oxygen supply to avoid interruptions in therapy. Maintain open communication with the home medical equipment provider to address any concerns or request timely refills or replacements.
Tips for Living Comfortably with Oxygen at Home
Many people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary fibrosis and other lung diseases eventually require supplemental oxygen therapy to reduce breathlessness. However, receiving a prescription for home oxygen can feel distressing. Suddenly, everyone who encounters you will know you have some sort of medical condition that requires you to use more oxygen.
As you navigate the challenges of setting up and using home oxygen therapy, remember it can greatly improve your quality of life as your COPD, pulmonary fibrosis or other lung disease progresses.
1. Talk with family and friends in advance
The first time your lung doctor brings up the topic of oxygen therapy, go home and have a conversation with family members about just how much oxygen and this will affect your life. Let them know the oxygen will allow you to stay active and continue to do the things you enjoy doing with them.
Ask for their support as you learn to adapt to using home and portable oxygen. These conversations may help keep life as normal as possible as you get started on oxygen therapy.
2. Understand your concentrator’s maintenance requirements
Many people receive an oxygen concentrator for home oxygen therapy. This machine can reside in a discreet corner and deliver oxygen to your nose through a long tube that can reach throughout the home.
When the home oxygen supplier sets up your concentrator, talk to them about required concentrator maintenance. For example, concentrators with a filter require a periodic filter change.
3. Replace your tubing and cannulas on a schedule
Supplemental oxygen therapy uses two separate pieces of tubing: a long tube that connects to the concentrator or tank, and a nasal cannula that attaches to the tubing and delivers the oxygen to your nostrils. Ask your oxygen supplier how often to change the main tubing and the cannula.
In general, you should change the cannula frequently even if it does not appear to be soiled. The tubing should be changed every month or two.
4. Keep extra tubing and cannulas close at hand
Always keep extra oxygen tubing and cannulas within easy reach in case either item becomes damaged during use. It’s not difficult to accidentally run a vacuum cleaner over a section of tubing, for example, and cut it.
Having extra tubing nearby will help you avoid a disruption of oxygen flow.
5. Have a plan for power outages
If your home loses electricity, your oxygen concentrator may not work. To avoid losing your portable oxygen concentrator supply during a power outage, write down an action plan. Your plan should include switching immediately to a portable oxygen tank until your power is restored.
Should you run out of oxygen before the electricity comes back on, call for medical assistance. If you have the ability, some people choose to purchase a home backup generator.
7. Practice fire safety
Oxygen itself is not flammable or explosive, but oxygen concentrators and tanks both infuse the environment with oxygen. They can cause fires to burn much longer periods more rapidly than normal. Keep oxygen equipment such as tanks away from any source of open flame.
Ask your doctor or home oxygen supplier about safe cooking practices if you use a gas range. Above all, do not allow anyone to smoke in your oxygen-rich environment.
How oxygen concentrators work
An oxygen concentrator mask works by filtering out oxygen from the air. You then breathe in the oxygen through small tubes that fit inside your nose (nasal cannulae).
The concentrator is roughly the size of a big suitcase and plugs into a normal electricity socket. Tubing from the machine can go along the floor or skirting board, and supplies oxygen from 2 different points downstairs.
It is also possible to have an extra supply point upstairs if you need it. The machine is very quiet. You have an emergency oxygen cylinder to use as back up, in case the machine breaks down.
How to get an oxygen concentrator
An oxygen supply company supplies the oxygen concentrator and all other equipment you need.
First, you need to sign a consent form allowing your doctor to send your contact details to the company. The company then contacts you to arrange a visit to install the machine.
How to get an oxygen supply
In England and Wales, 4 large companies are responsible for supplying you home oxygen service either with cylinders or a concentrator. They are responsible for everything to do with your oxygen supply, including providing a contact number in case you have any problems.
There are 3 types of devices that can be used to get enough oxygen to give you oxygen:
- an oxygen concentrator
- large oxygen cylinders
- portable cylinders
An engineer will install the equipment and explain how to use it safely.
Oxygen concentrator machine
An oxygen concentrator is recommended if you need to have oxygen for most of the day (including when you’re asleep).
The machine is a device about the size of a home printer and plugs into an electrical socket.
Large oxygen cylinders
Oxygen cylinders will probably be prescribed if you only need oxygen for a short time – for example, if you need to relieve sudden periods of breathlessness.
Portable oxygen cylinders
It may be possible to use a small, portable oxygen cylinder outside your home. This is called portable oxygen or ambulatory oxygen.
Most small portable oxygen cylinders only weigh around 2kg and are small enough to fit inside a small backpack or shopping trolley. This size cylinder holds just under 2 hours’ worth of oxygen.
Portable oxygen cylinders are not suitable for everyone.
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy at home equipment has revolutionized the way individuals receive essential oxygen therapy. With equipment such as oxygen concentrators, cylinders, and liquid oxygen systems, patients can experience increased independence, enhanced comfort, and improved quality of life. By working closely with healthcare providers and following proper care guidelines, individuals can enjoy the benefits of oxygen therapy in the familiar and comforting surroundings of their own homes.